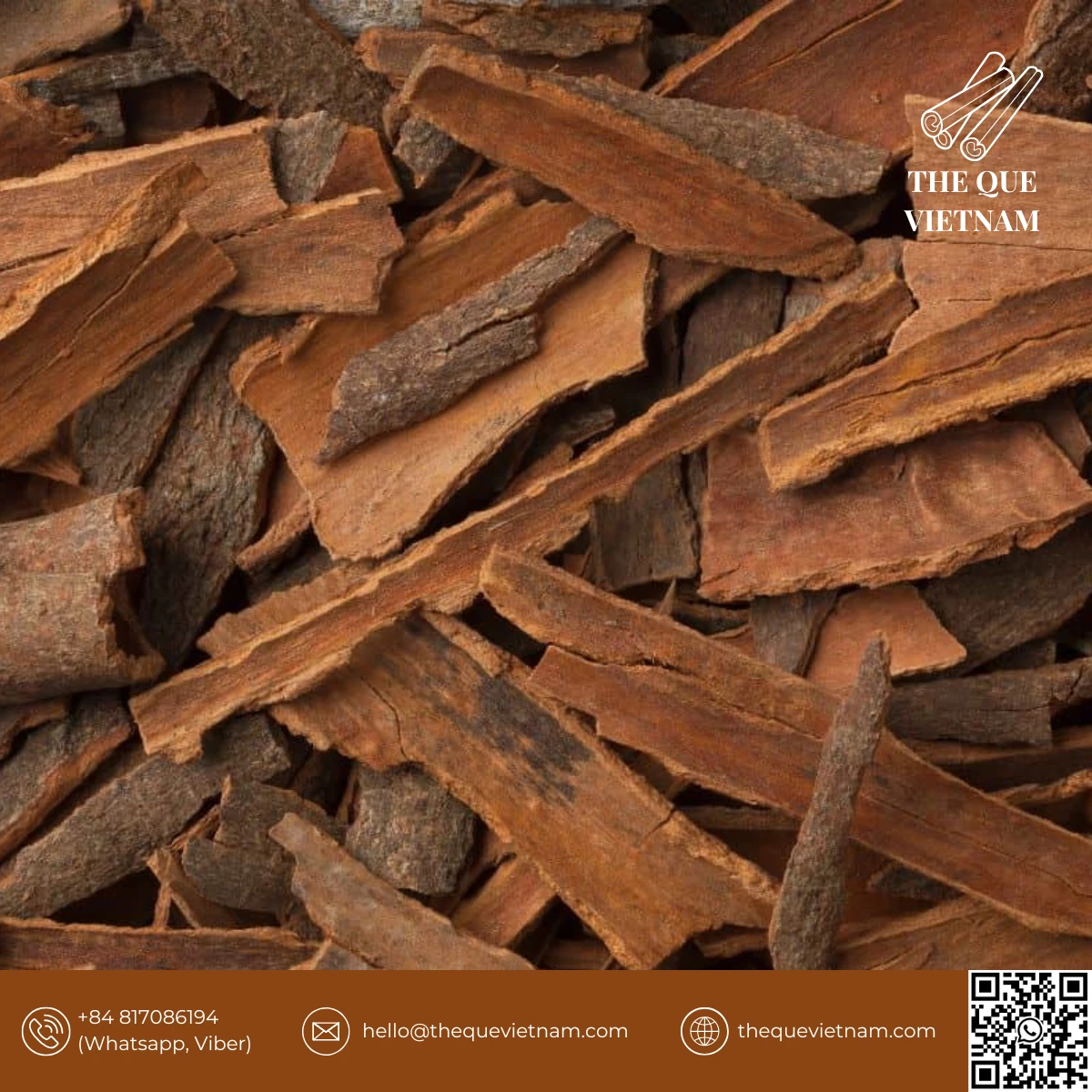
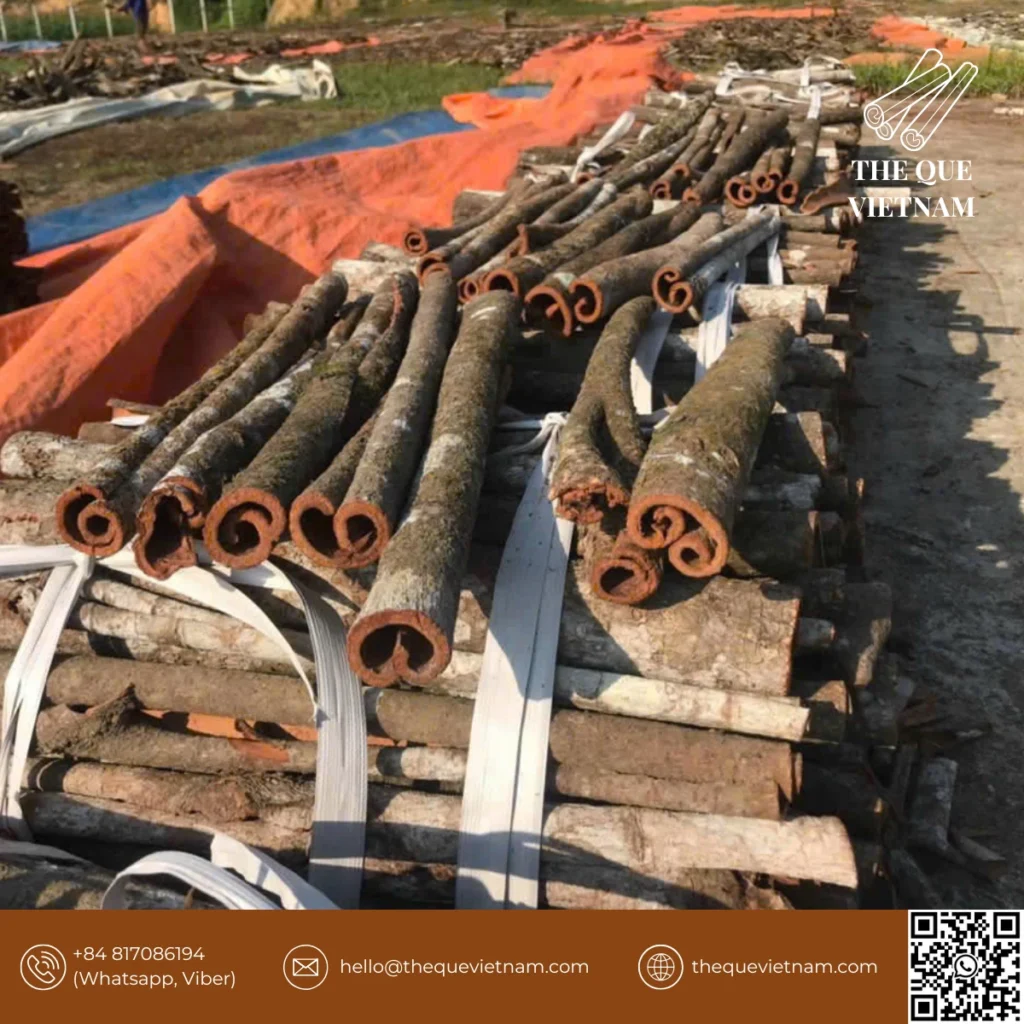
The Vietnamese cinnamon supply chain typically includes cultivation, harvesting, drying, sorting, quality control, packing, and export preparation. Each stage affects aroma stability, moisture levels, and shipment reliability, making supply chain management a critical factor for international buyers.
Cinnamon Supply Chain Explained: From Vietnam Farms to Export
For international buyers, sourcing cinnamon successfully is not only about origin or price — it is about how the supply chain is managed from harvest to shipment.
Understanding the cinnamon supply chain helps importers assess risk, consistency, and long-term reliability, especially when sourcing from Vietnam.
This article explains how the Vietnamese cinnamon supply chain typically works, with a focus on export-grade cassia cinnamon.
Vietnamese Cinnamon Supply Chain: Step-by-Step Process Overview
The Vietnamese cinnamon supply chain follows a sequential process where each stage directly affects export quality, shipment stability, and buyer outcomes.
Below is a simplified, end-to-end explanation of how cinnamon typically moves from farm to export.
Cultivation → Harvest → Drying → Sorting & Cutting → Quality Control → Packing → Export
1. Cinnamon Cultivation in Vietnam
Cinnamon trees in Vietnam are cultivated primarily in mountainous regions where climate and soil conditions support bark development.
Key factors at this stage include:
-
tree maturity at harvest
-
seasonal timing: a Spring Crop (February-April) and an Autumn Crop (July-September)
-
farming practices that affect bark thickness and oil development
For buyers, these factors influence quality consistency across harvests.
2. Harvesting & Bark Collection
Cinnamon is harvested by carefully removing bark from mature trees.
At this stage:
-
improper harvesting can damage bark quality
-
timing affects aroma intensity
Experienced harvesting practices are critical for maintaining export-grade standards.

3. Drying & Stabilization
After harvest, cinnamon bark undergoes natural drying to:
-
reduce moisture content
-
stabilize aroma
-
prevent mold development
Drying is one of the most important stages for export quality, as improper moisture levels can lead to shipment rejection.
4. Sorting, Grading & Cutting
Once dried, cinnamon is:
-
sorted by size, thickness, and appearance
-
graded based on buyer specifications
-
cut into required forms (stick, tube, broken, square cut)
This stage determines whether cinnamon meets commercial and industrial requirements.
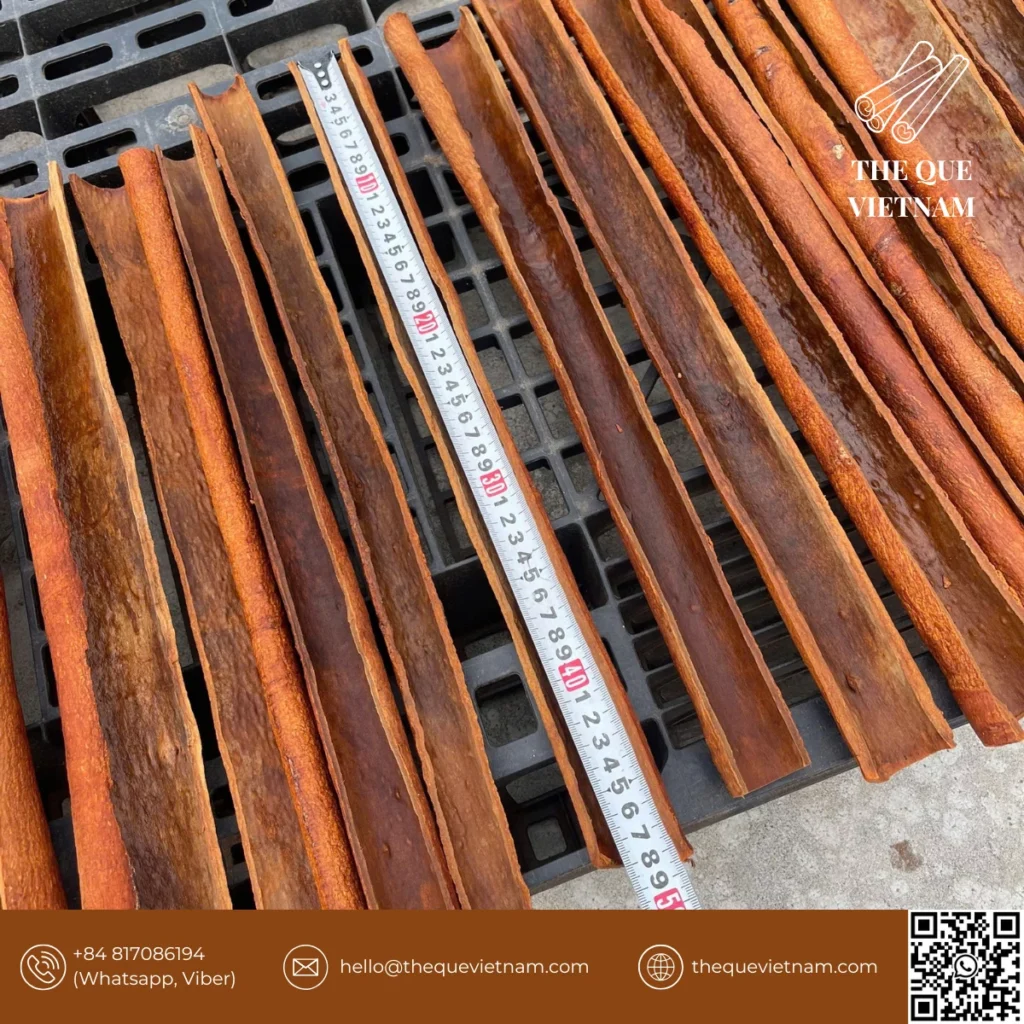

5. Quality Control Before Packing
Before packing, export-grade cinnamon is checked for:
-
moisture consistency
-
physical integrity
-
compliance with buyer specifications
Quality control at this stage reduces downstream issues during customs clearance and processing.
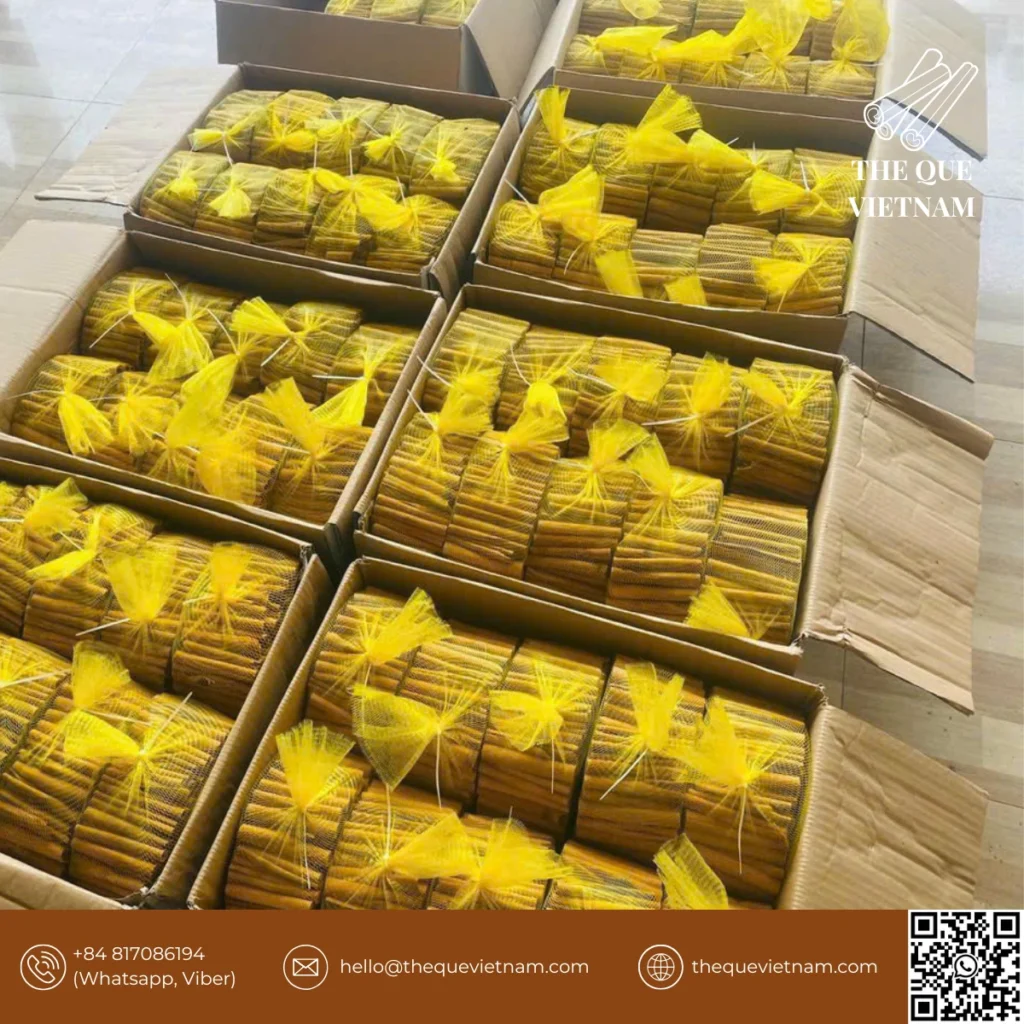
6. Packing & Export Preparation
Cinnamon is packed according to export requirements, which may vary by destination market.
Proper packing protects:
-
product integrity
-
aroma stability
-
shipment safety
Export documentation is prepared in parallel to ensure smooth logistics.

Key Risk Points in the Cinnamon Supply Chain
Understanding where risks occur in the cinnamon supply chain helps buyers evaluate suppliers more effectively and reduce downstream issues.
Key risk points include:
-
Harvest timing inconsistencies
Cinnamon harvested too early or too late can result in uneven bark thickness, weaker aroma, or inconsistent appearance across batches. -
Improper drying and moisture control
Inadequate drying may leave excess moisture in the bark, increasing the risk of mold growth, aroma loss, or shipment rejection during transit. -
Inadequate sorting and grading
Poor sorting can lead to mixed grades within a shipment, affecting processing performance and product consistency for manufacturers. -
Insufficient quality control before packing
Without proper checks, issues related to moisture, breakage, or foreign matter may only be discovered after shipment. -
Poor packing and handling
Incorrect packing materials or methods can compromise aroma stability and physical integrity, especially during long-distance transport.
For importers, these risks are best managed by working with suppliers who understand each stage of the supply chain and can clearly explain how quality is controlled throughout the process.
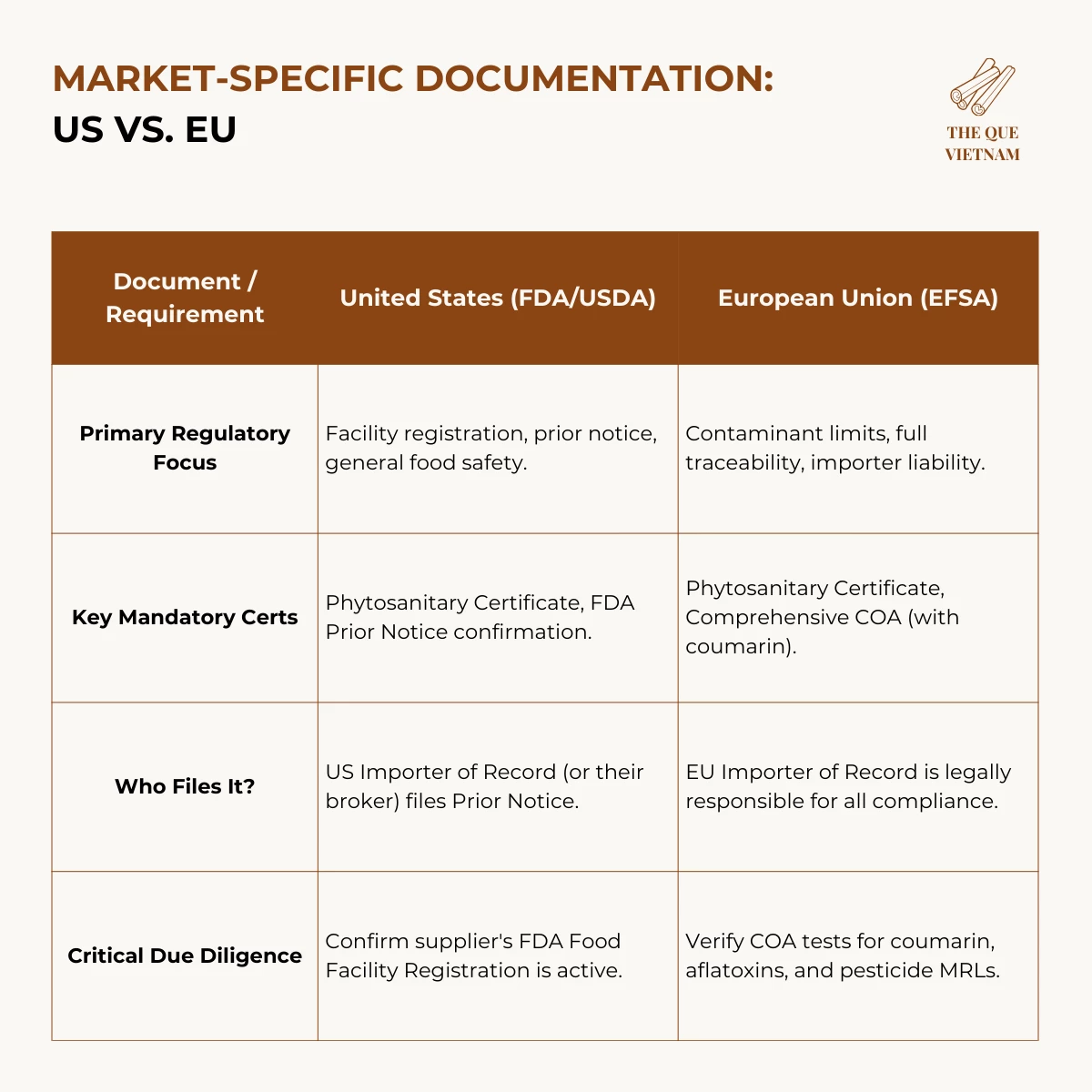
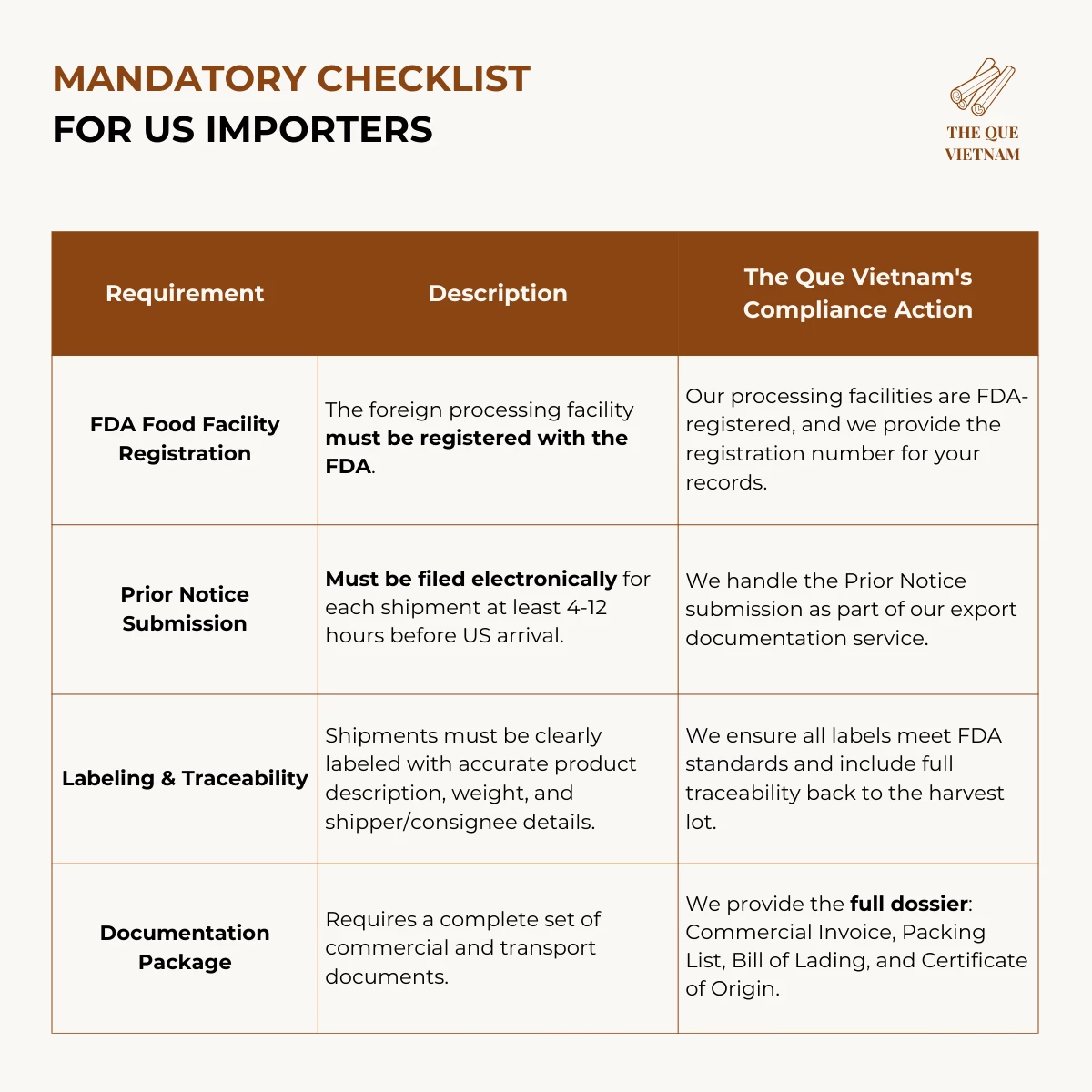
Export Requirements Buyers Should Understand
When sourcing cinnamon from Vietnam, buyers should be aware of several common export considerations that affect shipment success and compliance.
Key export requirements typically include:
-
Moisture expectations
Export-grade cinnamon is prepared with moisture levels suitable for international shipment to minimize the risk of mold and quality deterioration. -
Cleanliness and physical standards
Cinnamon intended for export is expected to meet cleanliness and physical integrity requirements appropriate for food manufacturing and further processing. -
Packing and labeling requirements
Packing formats and labeling may vary depending on destination market and buyer specifications, making early alignment important. -
Export documentation readiness
Proper documentation is essential for smooth customs clearance and logistics coordination. -
HS code classification
Export-grade cinnamon from Vietnam is typically classified under HS code 0906, which is used globally for customs and trade documentation.
Understanding these requirements helps buyers reduce delays, avoid compliance issues, and ensure consistent product performance across shipments.
Why Supply Chain Transparency Matters to Buyers
For importers, supply chain visibility helps:
-
reduce supply risk
-
improve planning accuracy
-
ensure consistent product performance
Suppliers who understand and manage these stages effectively are better positioned for long-term partnerships.
Final Thoughts
A reliable cinnamon supply chain is built on process control, not assumptions.
For buyers sourcing from Vietnam, understanding how cinnamon moves from farm to export provides a clearer basis for evaluating suppliers and managing risk.
Follow The Que Vietnam on Linkedin & Facebook for most updated news!

Frequently Asked Questions About the Cinnamon Supply Chain
The cinnamon supply chain from harvest to export typically takes several weeks to a few months, depending on harvest timing, drying conditions, and buyer specifications.
Key time variables include natural drying duration, sorting and grading requirements, and export documentation preparation. Buyers sourcing export-grade cinnamon should account for this timeline when planning production schedules.
Quality variation most commonly occurs during:
- Harvest timing, which affects bark thickness and aroma
- Drying, where improper moisture control can cause mold or aroma loss
- Sorting and grading, especially if specifications are unclear
Consistent quality depends on controlling these stages rather than relying solely on origin.
Drying is critical because it:
- Reduces moisture to export-safe levels
- Stabilizes aroma and oil content
- Prevents mold growth during transit
Improperly dried cinnamon can lead to shipment rejection, quality claims, or customs issues, making drying one of the most important steps in the export process.
Buyers can assess supply chain transparency by:
- Requesting clear descriptions of processing stages
- Confirming quality control checks before packing
- Reviewing consistency across shipments
- Evaluating documentation readiness for export
Suppliers who understand and explain their supply chain clearly are generally better positioned for long-term partnerships.
Buyer specifications should be defined before sorting and cutting, not after packing.
Clear requirements for grade, cut size, moisture level, and packing format help ensure the cinnamon supplied matches the intended application and reduces rework or disputes.
Pre-export quality control helps ensure:
- Moisture consistency across batches
- Physical integrity of cinnamon sticks or cuts
- Alignment with buyer specifications
This step minimizes issues during customs clearance and downstream processing.
No. Export requirements can vary by destination market, particularly regarding:
- Packing format
- Documentation
- Quality and cleanliness expectations
Understanding these differences is important when sourcing cinnamon for specific regions.
Supply chain visibility helps importers:
- Reduce supply risk
- Improve forecasting accuracy
- Maintain consistent product performance
For buyers managing long-term supply contracts, transparency is often as important as price.